The 3D printing market sees a regular emergence of new materials, which can make choosing the ideal materials for your parts a challenge.
In the case of FDM (fused deposition modeling) 3D printing, PLA and ABS have historically been the two main polymers that manufacturers turn to, though there is now a wide range of materials available. Many of these are playing critical roles in the future of FDM.
We continuously see new products become more popular, including both pure polymers and composites. In this article, we focus on the main pure plastics that exist in the market today, including PLA, ABS, PET, Nylon, TPU (Flexible) and PC. Material suppliers often provide blends or additives for modifying the properties of pure polymers, though these are not covered here.
Choosing the right polymer is essential for getting the right properties for a 3D printed part, especially if your part will be functional. Let’s break down the pure polymers we offer at Protolabs Network.
How do we grade FDM 3D printing filament materials?
Materials are usually graded along 3 categories: mechanical performance, visual quality, and process. In this case, we further break down these categories to paint a clearer picture of the polymer’s properties. The choice of material really depends on what the user wants to print, so we listed the key decision criteria needed to choose a material (other than cost and speed):
-
Ease of printing: This is how easy it is to print in a material, with factors including bed adhesion, max printing speed, frequency of failed parts, flow accuracy and ease of feeding into the printer.
-
Max stress: The maximum stress an object can withstand when slowly pulling on it.
-
Elongation at break: The ratio between the initial length and the changed length after an object breaks. It’s also called fracture strain.
-
Impact resistance: The energy required to break an object with a sudden impact.
-
Layer adhesion (isotropy): This is how well the layers of material adhere to one another. It’s linked to isotropy (uniformity in all directions). The better the layer adhesion, the more isotropic your part will be.
-
Heat resistance: The max temperature an object can withstand before softening or deforming.
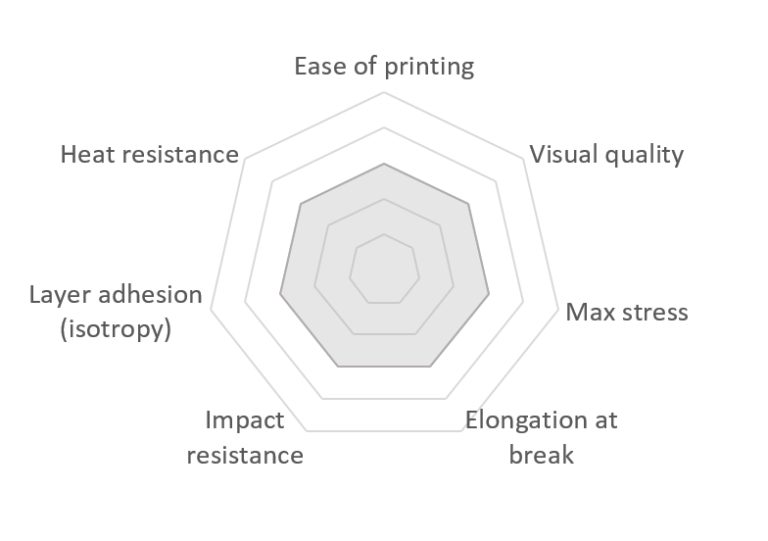
We have ranked each material with the following criteria on a simple scale (low to high). These are relative grades for the FDM process—they would look quite different if other manufacturing technologies were taken into account. Using data from Optimatter, the polymers have been ranked along the different criteria considered.
As a reminder, the grades given in this article are for an average polymer representing the general chemistry, but the performance will vary depending on the actual product or supplier.
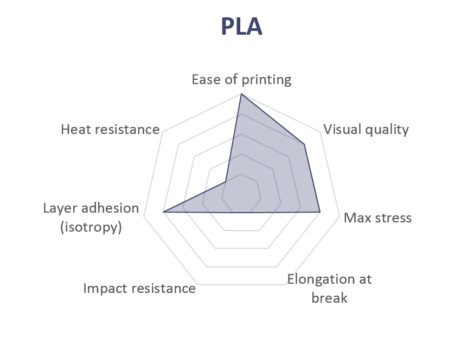
What is PLA?
PLA is the easiest polymer to print and provides good visual quality. It is very rigid and actually quite strong, but is very brittle.
PLA is bio-sourced and biodegradable, has good UV resistance and can be post-processed with sanding paper and painted with acrylics. It's also distinctly odorless. On the flip side, PLA does have low humidity resistance and can't be glued easily
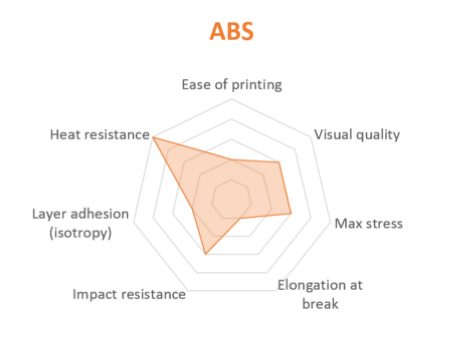
What is ABS?
ABS is usually picked over PLA when higher temperature resistance and higher toughness are required. It has good abrasion resistance, can be post-processed with acetone vapors for a glossy finish and can be post-processed with sanding paper and painted with acrylics.
ABS is sensitive to UV and potentially comes with high fume emissions. It develops an odor during the printing process.
What is PET?
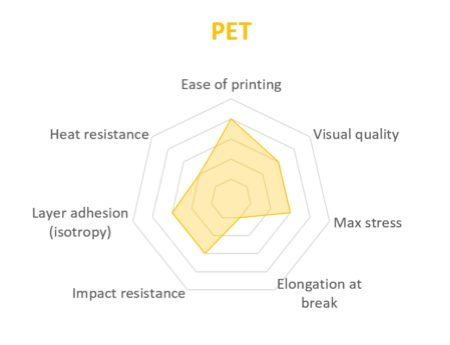
PET is a slightly softer polymer that is well rounded and possesses interesting additional properties with few major drawbacks.
Aside from its high resistance to humidity and chemicals, PET is also safe to come into contact with foods, is recyclable and has noteworthy abrasion resistance. Like the materials listed previously, it can be post-processed with sanding paper and painted with acrylics.
The only notable drawback is that it's heavier than PLA and ABS.
What is Nylon?
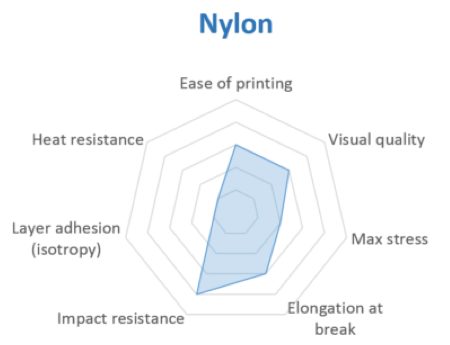
Nylon possesses great mechanical properties, and in particular, the best impact resistance for a non-flexible filament. It has excellent chemical resistance and is very strong.
For Nylon, layer adhesion can be an issue. The material absorbs moisture and printing with it has the potential to release emissions.
In this analysis, we’re talking only about Nylon 6. We aren't covering Nylon 11 and 12 here.
What is TPU?
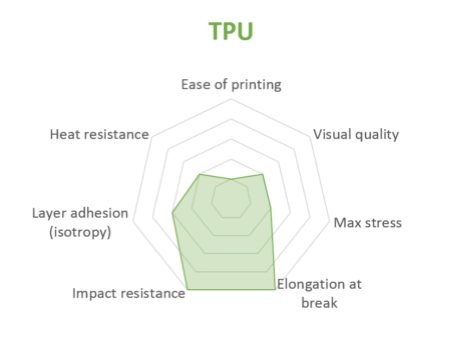
TPU is mostly used for applications where material flexibility is required, though it also sports very high impact resistance. It's quite abrasion-resistant and isn't affected significantly by coming in contact with oil and grease.
However, TPU is difficult when it comes to post-processing and cant' be glued easily.
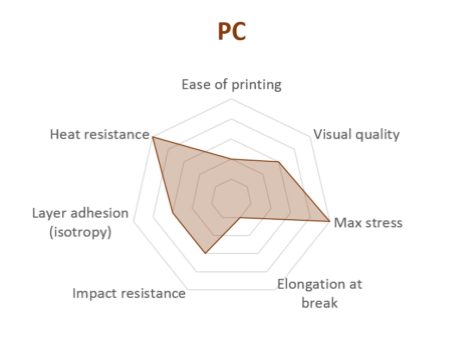
What is PC?
PC (polycarbonate) is one of the strongest materials of all for FDM 3D printing and can be an interesting alternative to ABS as the properties are quite similar.
The material can be sterilized and is easy to post-process, though it is UV sensitive.
Ready to start producing custom parts with FDM 3D printiong?
Frequently asked questions
What materials can be printed using FDM?
FDM 3D printing can produce parts in a wide range of filament materials. The most common are ABS, PLA and the blends created by material producers. More advanced (and more industrial) FDM printers can use specialized materials that provide benefits like rigidity and higher heat, impact and chemical resistances.
What are the most common filament materials for 3D printing with FDM?
What is the strongest filament material for FDM?
The strongest filament material for FDM at the moment is Ultem 1010. It’s a high-performing PEI thermoplastic that can withstand steam autoclaving and has high thermal stability. If you’re looking for the highest heat and chemical resistances, as well as tensile strength, of any FDM thermoplastic, then ULTEM 1010 is your go-to.
What materials are not used in FDM 3D printing?
You can’t produce parts with FDM using thermosets, as they degrade when heating, instead of melting.